“The development of full artificial intelligence could take us to the point where machines have self-awareness, consciousness, and the ability to think and feel.” – Elon Musk
Elon Musk, a visionary entrepreneur and outspoken advocate for AI ethics, speculates about the Future Potential of AI. His quote poses thought-provoking questions about the prospective emergence of AI systems with self-awareness and cognitive abilities similar to humans. It reminds us of the philosophical and ethical considerations that arise with the advancement of AI.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) have emerged as transformative forces, revolutionizing the way we live and interact with machines. From virtual personal assistants to self-driving cars, AI and ML are reshaping our world and redefining the possibilities of what intelligent machines can achieve.
Today we will be going through a combination of the un-ending horizon of opportunity and capabilities of AI with Intelligent Systems. We will be reading about Intelligent Systems in AI.
Table of Contents
What are Artificial Intelligence and Machine learning?
Firstly, Let’s start by understanding, what is Artificial Intelligence and then jump onto Intelligent Systems in AI.
Artificial intelligence is a broad field, which refers to the use of technologies to build machines and computers that have the ability to mimic cognitive functions associated with human intelligence, such as being able to see, understand, and respond to spoken or written language, analyze data, make recommendations, and more.
Although artificial intelligence is often thought of as a system in itself, it is a set of technologies implemented in a system to enable it to reason, learn, and act to solve a complex problem.
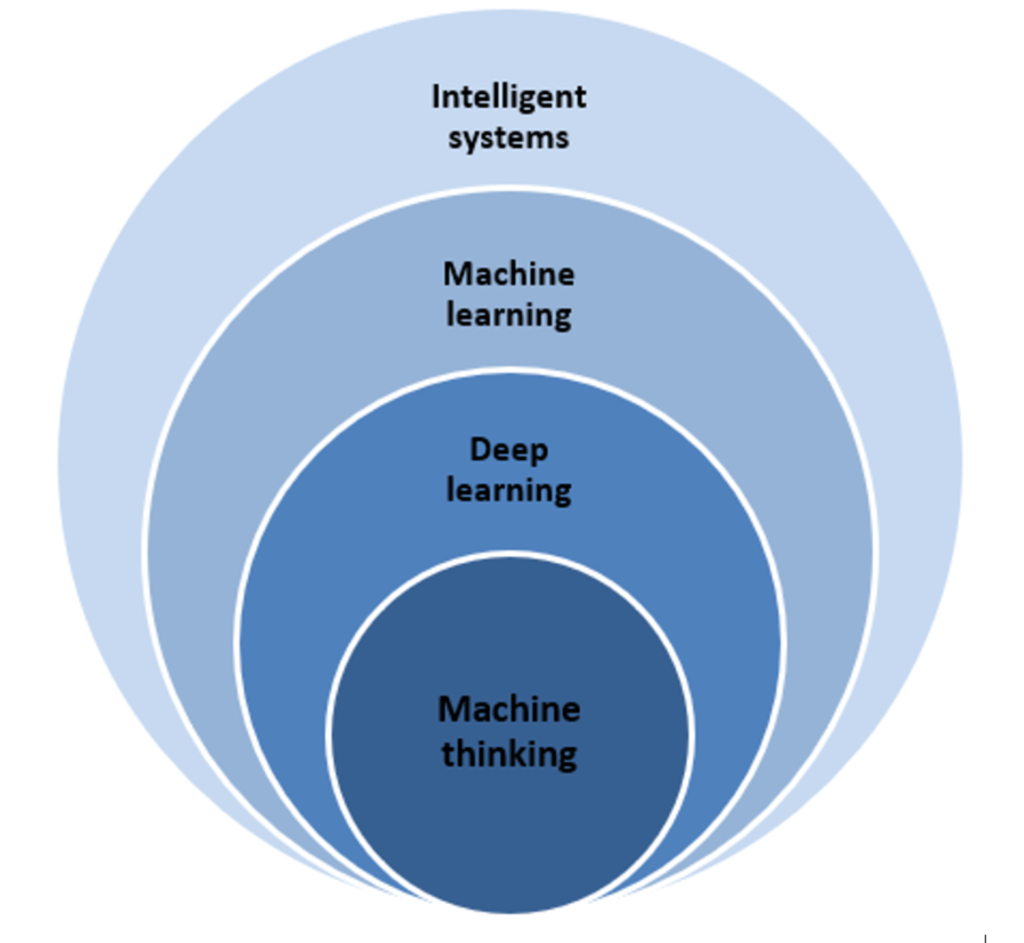
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that automatically enables a machine or system to learn and improve from experience. Instead of explicit programming, machine learning uses algorithms to analyze large amounts of data, learn from the insights, and then make informed decisions.
Machine learning algorithms improve performance over time as they are trained—and exposed to more data. Machine learning models are the output, or what the program learns from running an algorithm on training data. The more data used, the better the model will get.
What are intelligent systems?
An intelligent system is an advanced computer system that can gather, analyze, and respond to the data it collects from its surrounding environment. It can work and communicate with other agents, such as users or other computer systems. It can also learn from experience and adapt according to current data. An intelligent system might also support remote monitoring and management.
There is no single definition for an intelligent system. The term is applied in different ways by various sources.
For example, a Roomba vacuum is often referred to as an intelligent system. However, some could argue that its limited capacity to learn, such as its inability to avoid the same obstacle, disqualifies it from this category. On the other hand, most would consider a self-driving car to be an intelligent system or a valid attempt at an intelligent system.
Applications of Intelligent Systems in AI
AI has advanced tremendously in recent years, progressing from simple algorithms to more complex and intelligent systems. Machine learning is a crucial innovation that is contributing to the progress of AI. This technique allows AI systems to learn from data, detect patterns, and anticipate outcomes without the need for explicit programming.
In healthcare, Intelligent Systems are being used to analyze medical images, diagnose diseases, and personalize treatment plans based on patient data. They can sift through vast repositories of medical literature to assist healthcare professionals in staying abreast of the latest research and clinical guidelines. Moreover, wearable devices equipped with AI algorithms can monitor vital signs, detect anomalies, and alert users and healthcare providers to potential health issues in real-time.
In the realm of finance, Intelligent Systems in AI are transforming how we manage investments, detect fraudulent activities, and assess creditworthiness. They can analyze market trends, historical data, and news articles to generate investment recommendations and optimize trading strategies. Additionally, AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are revolutionizing customer service in the banking and insurance sectors, providing personalized assistance and resolving queries around the clock.

Furthermore, Intelligent Systems in AI are redefining how we interact with machines in our everyday lives. Voice assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant have become ubiquitous, enabling us to perform tasks, access information, and control smart devices using natural language commands. These systems leverage natural language processing and speech recognition technologies to understand and respond to user queries, facilitating seamless human-machine interaction.
In recent years, deep learning has taken AI to even greater heights. Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks, inspired by the human brain, to process vast amounts of data. This approach has proven to be remarkably effective in tasks such as image and speech recognition. Deep learning algorithms have enabled AI to understand and work with unstructured data, making it even more versatile and capable.
Fostering Creativity and Innovation
Fostering creativity and innovation stands as a pivotal advantage in the era of AI-driven human-machine collaboration. This synergy empowers both individuals and organizations to expand the horizons of possibility by leveraging the distinct strengths of humans and machines. Here are some key considerations highlighting how human-machine collaboration contributes to enhancing creativity and innovation:
- Insights from Data: AI systems excel in analyzing extensive datasets, uncovering patterns, trends, and anomalies that may elude human perception. This capacity for data analysis serves as a wellspring of inspiration, equipping humans with data-driven insights to inform their creative decision-making processes.
- Idea Cultivation: AI algorithms can be tailored to generate ideas and concepts across various domains such as design, content creation, and problem-solving. For instance, in design tasks, AI can propose alternative design elements, layouts, or color palettes based on historical trends and user preferences.
- Streamlined Efficiency and Automation: AI technologies streamline repetitive and time-intensive tasks, allowing human professionals to redirect their focus toward more creative and strategic endeavors. As mundane tasks are automated, individuals can invest their time and energy in exploring fresh concepts and pushing the boundaries of innovation.
Augmented Decision-Making
- Enhanced Data Analysis: Augmented decision-making leverages AI to analyze vast datasets quickly and accurately, providing decision-makers with comprehensive information.
- Real-time Insights: AI systems can process data in real-time, allowing decision-makers to respond rapidly to changing situations.
- Improved Accuracy: By reducing the potential for human error, augmented decision-making can lead to more precise and consistent decisions.
- Contextual Understanding: Humans provide the critical context and nuanced understanding necessary to make well-informed decisions.
- Ethical Considerations: The collaboration between humans and AI must consider ethical implications and ensure responsible decision-making.
- Risk Management: Augmented decision-making can help identify and mitigate risks more effectively, safeguarding businesses and organizations.
The Complication: Limitations and Ethical Concerns regarding Intelligent Systems.
Despite promising advances, AI has limits and ethical challenges that require immediate attention. The reliance on data is one significant concern. AI systems learn from the data that is provided to them. If the data is inaccurate or inadequate, it might lead to distorted results or confirm preexisting preconceptions.
In employment procedures, for example, AI systems may unwittingly perpetuate prejudices existent in past data. This might lead to biased judgments being made against specific groups, limiting diversity and fairness in job prospects. To address this prejudice, a thorough study of the data used to train AI models is required, as is the development of tools to reduce these biases.
- Bias and Equity: AI systems have the capacity to internalize biases from the data on which they are trained. Ethical dilemmas emerge when these biases contribute to discrimination, especially in critical domains like employment, financial services, and law enforcement. Addressing biases and ensuring equity in AI algorithms presents a significant ethical imperative.
- Privacy Concerns: AI applications often entail the gathering and analysis of extensive datasets. Safeguarding individuals’ privacy stands out as a paramount concern, particularly in light of potential harm resulting from data breaches or unauthorized exploitation of personal information. Ethical AI frameworks must prioritize both data security and user consent.
- Responsibility and Accountability: Determining culpability for AI-generated decisions can be intricate. Establishing transparent lines of accountability is essential to rectify errors or unethical behaviors exhibited by AI systems. This necessitates delineating legal and ethical obligations for AI outcomes.
- Transparency Imperatives: AI algorithms are frequently perceived as opaque “black boxes,” making it challenging to comprehend the rationale behind specific decisions. Ethical standards mandate transparency, requiring developers and organizations to furnish explanations for the decisions driven by AI.
- Workforce Displacement Concerns: With the advancement of AI and automation, apprehensions arise regarding the potential displacement of human workers. Ethical considerations encompass implementing retraining and upskilling initiatives to mitigate adverse impacts on the workforce.
- Ethical Data Utilization: The acquisition, retention, and application of data raise pertinent questions about the legitimacy of its collection and usage. Employing data unethically, such as for surveillance purposes or discriminatory practices, emerges as a significant ethical quandary.
Is Humanity Prepared for the Era of Conversational AI?
The advent of Conversational AI marks a significant shift in human-machine interaction, fundamentally altering the way we engage with technology, conduct online activities and access information. Integrating natural language processing, machine learning, and other AI methodologies, Conversational AI systems have rendered human-tech exchanges more seamless, intuitive, and tailored. From voice assistants to chatbots, these AI innovations elevate user experiences, redefine customer support standards, and optimize business workflows.
As we conclude, we want to thank you for being a part of The TechInsider community. We’re committed to keeping you updated on the latest tech trends and innovations. With our team of experts, we strive to provide timely and insightful content that empowers you to stay ahead in the fast-paced world of technology. Your support drives us to explore new horizons and push boundaries. Together, let’s continue embracing the transformative power of technology. Stay informed, stay curious, and keep exploring with The TechInsider.
With that said if you want to know more about the uses of AI other than in Intelligent systems then make sure to check out this blog regarding Artificial Intelligence’s Adaptive Intelligence and Cognitive Computing: Revolutionizing Problem-Solving.




